In the current world, there are Four (4) Type of Electric Vehicle which you see on the road’s across the world and they are BEV, HEV, PHEV & FCEV
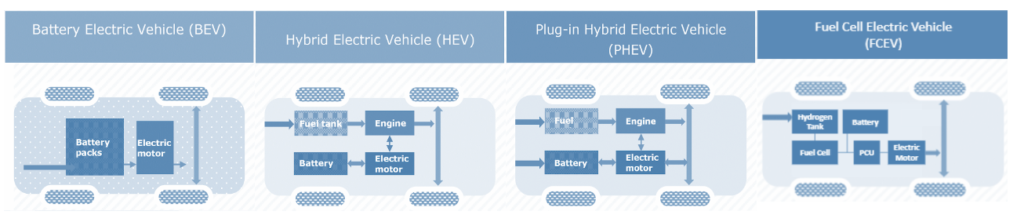
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Plugin Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
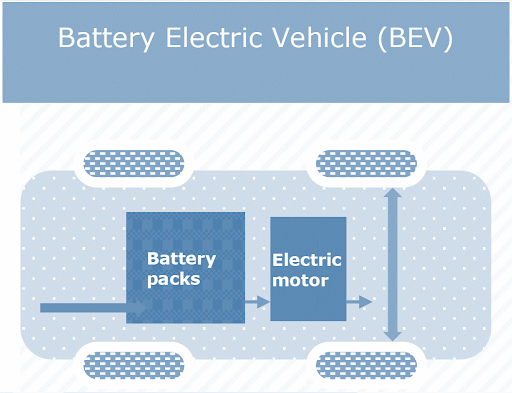
BEVs are often referred to as All-Electric Vehicles (AEV). BEV-powered electric vehicles rely fully on a battery-powered electric powertrain. The electricity needed to power the vehicle is stored in a big battery pack that can be charged by connecting to the power grid. The charged battery pack then powers one or more electric motors, which power the electric vehicle.
How Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) works?
The power for the electric motor is converted from the DC Battery to AC. As the accelerator is pressed, a signal is sent to the controller. The controller adjusts the speed of the vehicle by changing the frequency of the AC power from the inverter to the motor. The motor then connects and leads to the turning of wheels through a cog. If the brakes are pressed, or the electric car is decelerating, the motor becomes an alternator and produces power, which is sent back to the battery
Current BEV Electric Cars – MG ZS, TATA Nexon, TATA Tigor, Mahindra E20 plus, Hyundai Kona, Mahindra Verito
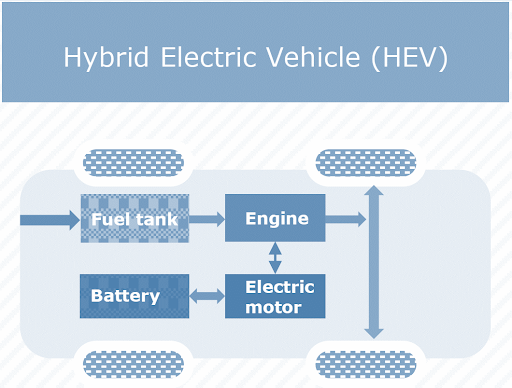
HEVs are sometimes referred to as series hybrids or parallel hybrids. HEVs are powered by both an engine and an electric motor. The engine is powered by fuel, while the motor is powered by batteries. Both the engine and the electric motor rotate the gearbox at the same time. This, in turn, drives the wheels.
How Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) Works?
The fuel tank supplies energy to the engine like a regular car. The batteries run on an electric motor. Both the engine and electric motor can turn the transmission at the same time.
Current HEV Products- Engine, Electric motor, Battery pack with controller & inverter, Fuel tank, Control module
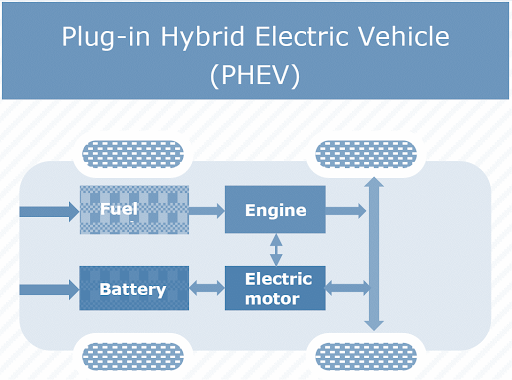
PHEVs are also referred to as series hybrids. They have an engine as well as a motor. You can pick between conventional fuel (such as gasoline) and alternative fuel (such as bio-diesel). A rechargeable battery pack can also be used to power it. External charging is possible for the battery.
There are difference way PHEV’s run a) All-electric Mode, in which the motor and battery provide all the car’s energy b) Hybrid Mode, in which both electricity and petrol/diesel are employed
How Plugin Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) Works?
PHEVs start in all-electric mode and run on energy until their battery pack runs out. When the battery is depleted, the engine takes control and the car works as a standard, non-plug-in hybrid. PHEVs can be charged using an external electric power source, engine, or regenerative braking. When the brakes are engaged, the electric motor serves as a generator, transferring energy to the battery. The electric motor supplements the engine’s power; as a result, smaller engines may be employed, boosting the car’s fuel economy without sacrificing performance.
Current PHEV Cars on the road – Porsche Cayenne S E-Hybrid, BMW 330e, Porsche Panamera S E-hybrid, Chevy Volt, Chrysler Pacifica, Ford C-Max Energi, Mercedes C350e, Mercedes S550e, Mercedes GLE550e, Mini Cooper SE Countryman, Ford Fusion Energi, Audi A3 E-Tron, BMW i8, BMW X5 xdrive40e, Fiat 500e, Hyundai Sonata, Kia Optima, Volvo XC90 T8.
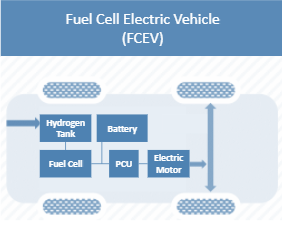
FCEVs are also known as Zero-Emission Vehicles. They employ ‘fuel cell technology’ to generate the electricity required to run the vehicle. The chemical energy of the fuel is converted directly into electric energy.
How Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) Works?
The FCEV generates the electricity required to run this vehicle on the vehicle itself.
Current FCEV Vehicle on the raod – Toyota Mirai, Riversimple Rasa, Hyundai Tucson FCEV, Honda Clarity Fuel Cell, Hyundai Nexo
Leave a Reply